A domain name is an integral part of a website, similar to our home address. It helps users to find your site on the web. So, it is very important to choose the right one, especially if you want to make your mark in the online world. Knowing all components of a domain name we can easily select a perfect on regarding our business name. Now, without wasting any further time, let’s dig in.
A website’s real address is a complicated set of numbers called an IP address (like 192.0.2.2). However, thanks to DNS, people can use easy-to-remember domain names to find the websites. This whole procedure is called a DNS lookup.
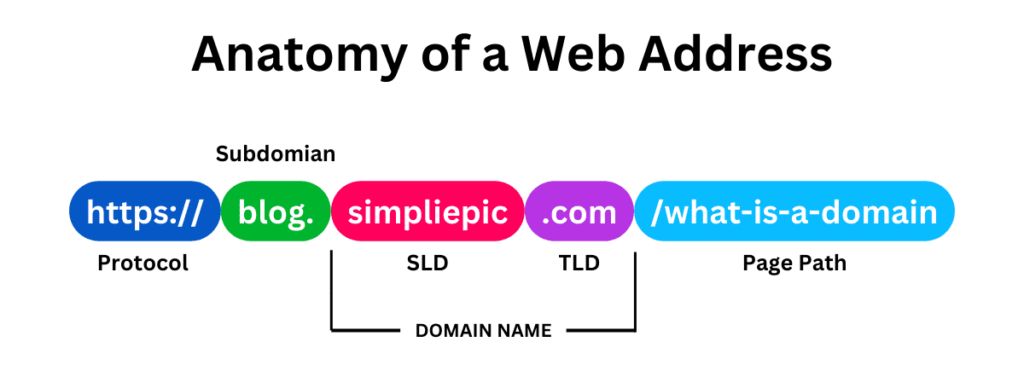
Main Components of a Domain Name | Domain Parts
A domain name consists of three key components or parts that work together to create a unique address for a website. These components include:
- Top-level domain (TLD)
- Second-level domain
- Subdomain or Third-level Domain
Now, let’s get comprehensive understanding of each one by one and with examples.
Top-level domain (TLD)
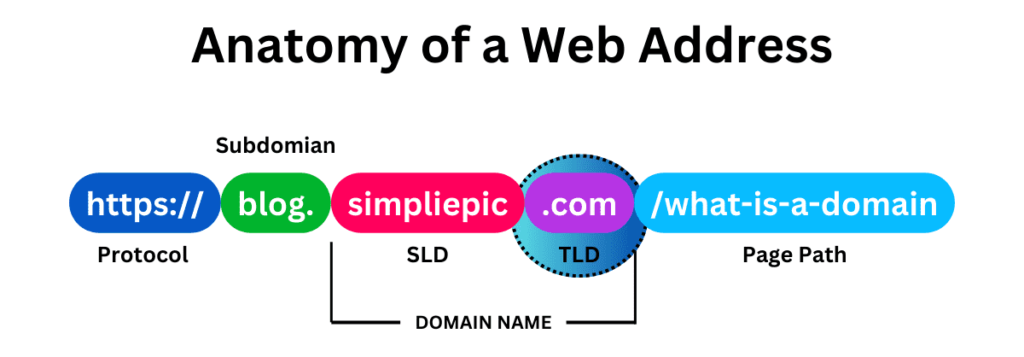
Introducing Top-Level Domains: Adding Meaning to Your Domain Name
The top-level domain (TLD), more commonly known as domain extensions, serves as the concluding part of a domain name, like .com or .org, and plays a vital role in providing context to the domain. It often indicates the nature of an organization or the associated country. For example, in the domain “skilleavor.com,” the TLD is “.com.”
There are various types of TLDs and each serve different purposes:
Generic Top-Level Domain (gTLD):
These are the most common TLDs. They are widely used by commercial websites and are not specific to any particular country or region. This type of TLDs include following domain extensions:
- .com (48% of websites globally use .com)
- .co (company, also used as the ccTLD for Colombia)
- .edu (education)
- .org (organization)
- .net (network)
- .biz (business)
- .gov (government)
- .info (information)
- .shop (ecommerce)
Keep in mind that not all generic top-level domains (gTLDs) operate like .com, which is open for anyone to register. Some, like .edu, is restricted for educational institutions, .gov, are reserved exclusively for government organizations and .pro, reserved for professionals who can verify their credentials.
Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs):
These TLDs are country-specific domain extensions. and are linked to specific countries or territories. Using these are best to market a website to a certain country or locale.
There are more than 200 country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) available. Typically, they consist of two letters from the Latin alphabet. This type of TLDs include following domain extensions:
- .us for the United States
- .jp for Japan
- .de for Germany
- .au for Australia
- .pa for Pakistan
- .uk for the United Kingdom
- .in for India
- .nz for New Zealand
There is an exception to this norm known as IDN ccTLDs (internationalized country code top-level domains). These domain extensions employ the native script of their respective countries.
For instance, China recognizes both its regular ccTLD, .CN, and its IDN ccTLD, .中国, which translates to “China.”
PRO TIP
Opting for a TLD (Top-Level Domain) other than .com for your business or niche can be highly advantageous. It sets you apart from the multitude of websites on the internet and allows your business to stand out more effectively.
Brand Top-Level Domains (bTLDs):
Custom TLDs owned by companies for exclusive use, such as .google for Google or .apple for Apple Inc.
Second-level domain
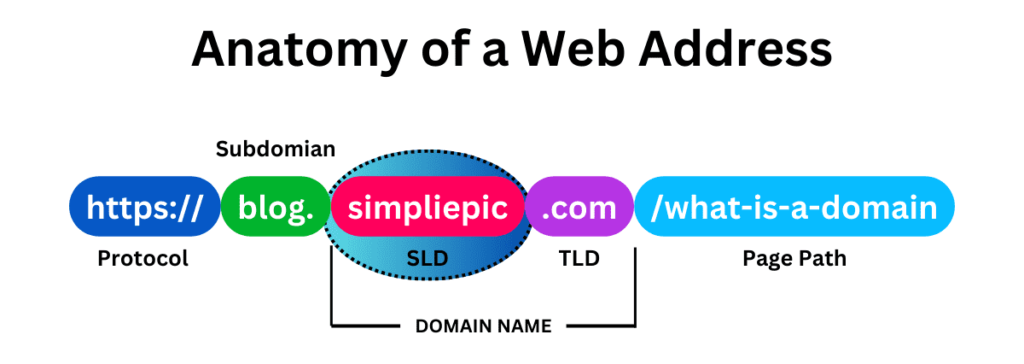
The second-level domain (SLD) represents the name of your website. It is the part of the domain name you can personalize to mirror your personal name, brand name, company name or the essence of your site. – Whatever suits your preferences.
For instance, in www.skilleavor.com, the second-level domain (SLD) is “skilleavor“.
As SLDs play an important role in making your domain name unique, there are some points, you should consider while choosing your domain name:
- Keep it short and simple, ideally between 6 to 14 characters.
- Opt for a name that is catchy and easy to remember.
- Avoid using complex words and punctuation
- Add a keyword relevant to your industry or niche.
- Experiment with the keyword + modifier formula, such as bestcooking.com or easycourse.uk.
- Make it creative
Subdomain or Third-level Domain
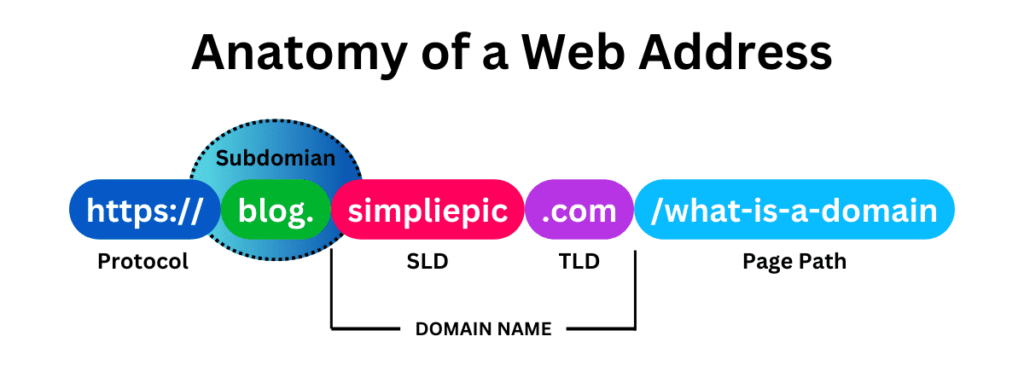
A subdomain is an additional prefix attached to a URL before the main domain name. For Example “blog.skilleavor.com”. It is use to create separate a section of your website without buying a new domain name. You do not need to use subdomains on your website. However, by using them, you can save money, improve your web development projects and manage extensive sections that require their own content hierarchy, such as shops, blogs, job boards or support platforms etc.
From a technical standpoint, www, which stands for World Wide Web, is the most common and popular subdomain. However, in this article, we will focus on other commonly used subdomain examples, like blog, shop, or support, as they are used to serve a specific function.
In this analogy, consider your website’s domain name as a street address. Subdomains would be the individual apartments at that address, each with its own distinct location, entrance and purpose.
For example:
- Blog: blog.example.com
Purpose: This subdomain can be use to dedicate a separate section for your blog posts, allowing you to organize and showcase your articles separately from the main website.
- Shop: shop.example.com
Purpose: If you want to add an online store associated with your domain, creating a subdomain like this can help you to manage and present your products distinctively instead of integrating the features and functionality with your main website.
- Support: support.example.com
Purpose: A support subdomain can be utilized for customer service, FAQs, or any content related to assisting users, keeping it separate from the main website.
- Events: events.example.com
Purpose: This subdomain can be used to highlight upcoming events, conferences, or any significant happenings associated with your organization.
Each subdomain functions as a separate section of your website, providing clarity and organization for both you and your visitors.
Conclusion
Domain names are fundamental to website identification and organization, and understanding their components is crucial for establishing a strong online presence with their own website or email address. It can also help to optimize the domain for search engines like Google, Bing etc. From the TLD to SLD and subdomain, each element plays an important role in shaping your online identity and accessibility. As in this article, we have covered everything from the basic structure of a domain name to the hierarchy of its all components and how it connects to the Domain Name System (DNS).
Now that you know what makes up a domain name and how it can shape and grow your business over time. Go ahead here and create one (in discounted price) that suits your business and brand the best. –BEST OF LUCK
FAQs
What does the top-level domain (TLD) represent?
The TLD is the ending part of a domain name, such as .com, .org, or .net. It provides context and indicates the type of organization or the country associated with the website.
What is the second-level domain (SLD) and its significance?
The SLD represents the name of your website and it is customizable part of a domain name, like “simpliepic” in “simpliepic.com.” Remember to personalize it according to your desired name, brand, or purpose of the website.
How do subdomains fit into the components of a domain name?
Subdomains are optional prefixes added to a URL before the main domain name. It provides a way to organize different sections of a website or to create distinct websites under the same domain without effecting the main website contents.
Why is it important to choose a memorable second-level domain (SLD)?
Selecting a memorable SLD is crucial as it enhances brand recognition and also makes it easier for users to remember and revisit your website.
In the domain name structure, what is the role of the domain name system (DNS)?
The DNS plays a vital role in converting easy-to-remember domain names into computer-readable IP addresses. This translation enables web browsers to accurately find and connect to the appropriate web server by converting domain names into IP addresses.


0 Comments